Commercial Pumps & VFD’s
Can I control the Viridian using a DC signal?
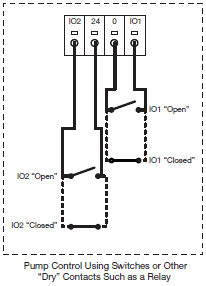
Yes, to do this you must set I1 to “No Function” and set I2 to “Run”. When above 8 volts DC (max 32 volts) is applied to IO2/24V, the pump will run. When below 2 volts DC is applied to IO2/24V, the pump will go into stand-by mode (Flashing blue light).
Can I modulate the speed of the Viridian externally?
No, the speed is determined internally within the pump’s brain. You can however control the pump externally via the digital inputs (turn on/off, and force the pump to run on maximum or minimum speed)
Can I use an external demand to “call” the Viridian pump on and off?
Yes, to do this, you must have a thermostat or an end switch trigger the pump to run. Next, power must always be applied to the pump comtrol. Now go into the programming of the Viridian and set I1 to “No Function” and set I2 to “Run”. Now you will have the ability to wire a switch across the IO2 and 24V terminals. When the circuit is closed, the pump runs (solid blue light) and when the circuit is opened, the pump goes into standby mode (flashing blue light).
Can I run the VR25 and VR30 down to 208 Volts?
In the VR25 and VR30, there was a change made to the internal fuse so they could operate down to 208V. The -1 versions of the VR25 and VR30 had a voltage range of 230V-240V. The -2 versions of the VR25 and VR30 (with the new fuse) now have a range of 208V-240V.
Can I use the alarm contacts from the Viridian to send a speed feedback signal to a DDC controller?
Yes, there are relay outputs (either NO or NC) that can monitor various pump operating functions. The factory default is “Error”. If the pump goes into an overload condition the relay will change position (NO will close and NC will open). The relay “trigger” can be changed to Run (or monitor if the pump is running), Off or position of digital input I2. The relay rating is 250 VAC, 8 Amps.
Can the 1900 series pump be installed with the motor in a vertical orientation?
Yes, the 1900 series pumps can be installed with the motor vertically oriented because it is a close coupled design. However, the similar 1600 pumps cannot be oriented vertically.
Can you vary the speed of the Viridian using a 0-10 Volt DC signal?
The Viridian is capable of being turned on and off using 0-10 Volt DC signal. You are not able to actually change the speed of the pump based on a change in the DC voltage. See “Can I control the Viridian using a DC signal?” in the Viridian FAQ section.
Can you vary the speed of the Viridian using a 0-10 Volt DC signal?
The Viridian is capable of being turned on and off using 0-10 Volt DC signal. You are not able to actually change the speed of the pump based on a change in the DC voltage. See “Can I control the Viridian using a DC signal?” in the Viridian FAQ section.
Do I need the internet to communicate with the Viridian?
Communication with the Viridian is done through an ethernet connection. The Viridian control is its own “intranet”. You do not use the actual internet to make this connection.
How do I communicate with the Viridian? (PC Windows 7 version and Mac.)
In order to communicate with a Viridian, you will need the following: Window 7 operating system, a CAT 4 or better ethernet cable and power to the pump. First you will need to set a ‘Static’ IP address on your computer. To do this, got to the Start Menu, then Control Panel. Go to Network and Internet, then open Network and Sharing Center. Select Change Adapter Settings and right click on a wired Local Area Connection and select Properties. In Properties, select Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4)and then select the Properties tab to the bottom right. Click on the radial ‘Use the following IP address’. In the IP Address space, type: 192.168.0.123 (The last 3 numbers can be any number 2-244). The Subnet mask will automatically be inserted. Select OK. You can now open a web browser ( Internet Explorer, Mozilla, Firefox, Safari, Chrome etc) and type in the address bar ‘192.168.0.245’ (245 is the factory default address for each Viridian) or ‘http://viridian’.
How do I find the IP address of my Viridian pump?
You can use any IP search program available online. Use a program called wireshark (you can use any other program that can look on at your network traffic). The program looks traffic on the network adapter, which you choose. It is preferred that you have the pump connected only an Ethernet cable and wireless turn off, so that you don’t have too much traffic. The pump is always looking for its twin pump, so it sends a transmission over the network in which it is asking: ?Who has xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx? Tell yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy? (where x is the IP of the twin, and y is your address).
Link: WireShark 1
Link: WireShark 2
Link: WireShark 3
How do I force the Viridian pump to run at maximum power?
To do this, leave the factory defaults, I1 to “Run” and I2 to Max”. Then, place a jumper across terminals IO2 and 24V (Solid blue light). To stop the pump, either remove the jumper between IO2 and 24 V or place the jumper between IO1 and OV to put into standby mode (flashing blue light).
How to control two Viridians with one control?
- If you want both pumps to be enabled when the boiler enable circuit is open, simply connect this to I01 and 0V terminals – factory default is OK as is. OR
- If you want both pumps to be enabled when the boiler enable circuit is closed, connect to I02 and 24V terminals. Factory defaults would have to be set Input I1 (I01) “no-function” and Input I2 (I02) set to “Run”. NOTE: Using the crossover Ethernet cable will have only one pump run and alternate (with both pumps enabled). If both are disabled, neither will run.
I have an old VL2508, what is the current replacement?
The current replacement vertical inline pump is the KV series. In order to select the correct model, the GPM and Head must be known along with the model pump you have.
Link: KV Series
Is additional support required when installing the 1600 Series circulators?
The 1600 series is a resilient mount design, to help reduce vibration transmitted into the piping. Resilient mount motor is supported by the bracket. If you apply an upward force on the bracket, either by a hanger or a foot support on the floor, it is possible to cause misalignment with the couplings, causing premature, uneven wear on the seal faces, and stress on the bearings. The piping should be rigid enough to support the overhung load of the motor, but be careful of torsional stress on the piping. To prevent that, you may have some type of foot support or hanger on the cast iron bracket, just adding some support.
Is the Viridian in the Taco selection software?
Yes, it is part of our selection software.
Minimum flow applications (low mass boilers for example).
For applications where minimum flow is a concern, the low flow differential head can be increased by increasing the H max or changing the slope of the pump curve (% proportional). In addition, the Viridian can be set to constant and any of the 12 speeds may be selected (more for constant flow applications).
My inline 1600 series pump has an Emerson motor on it. Is the motor warrantied by Emerson or Taco?
All 121-138 and 1600 series pumps utilizing an Emerson motor is covered by Taco Commercial Warranty. See attached.
Attachment: 1600 Series In-Line Pumps Warranty
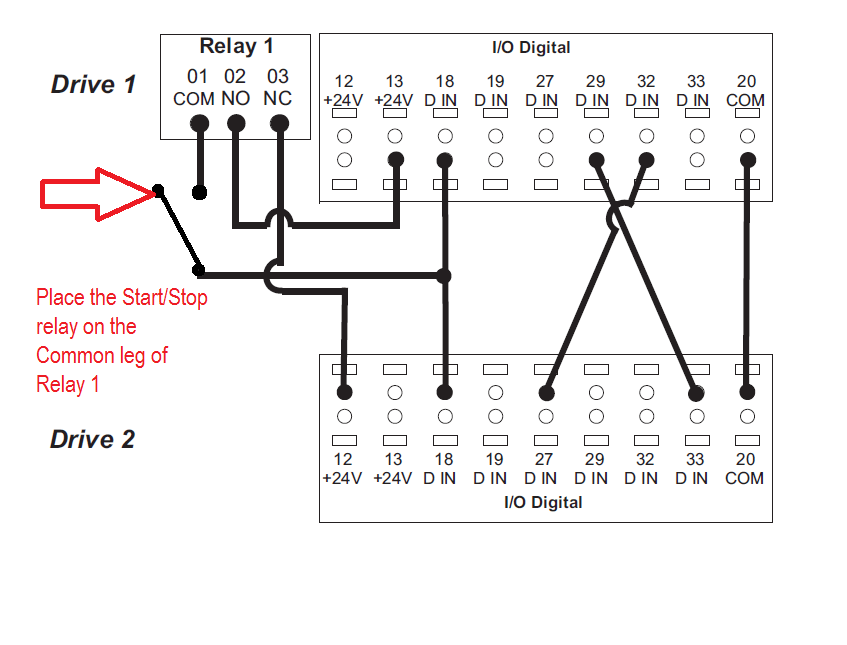
On an SKV or SKS wired in alternation, where can I apply a start/stop signal to control the pumps?
Using a dry contact relay make and break the Common terminal on Relay 1 that is wired between terminals 18 on each of the drives. See wiring diagram.
One of our process pumps will be taken out of service and put away for long-term storage. Any suggestions on proper storage?
Here are some general suggestions for long term storage. The applicability of all, or some, of these suggestions depends on several factors such as type of equipment, length of storage, and condition of the environment:
- Drain the casing completely and dry it thoroughly, including its bearing housing and stuffing box, or seal chamber. Apply a coat of soluble rust preventive solution both internally and externally.
- Cover all openings. Flanged openings (such as suction and discharge nozzles) should be covered with blind flanges with elastomer gasket. Threaded openings should be covered with steel plugs or caps.
- Remove the shaft coupling; it may cause the shaft to develop a permanent sag during prolonged storage.
- Wrap the exposed shaft and key with corrosion inhibitor waterproof paper or waxed cloth.
- Protect the bearing housing from moisture by placing bags of vapor phase inhibitor crystals around the housing.
- Cover the equipment with industrial strength plastic, preferably transparent to allow visual inspection, including its nameplate, without uncovering the unit.
- Store the unit in its normal position in a dry, clean place.
- Inspect the unit periodically and turn the shaft a few times plus 1/4 turn. Turning the shaft prevents pitting of finished surfaces. The extra 1/4 turn is to displace the sag and prevent the shaft from developing a permanent bow.
Overload protection – what, how and the effects (auto reset or manual).
Note each number below corresponds to the number of pulses of the red overload light on the face of the VFD:
- Low load (dry run) – pump shuts off after approximately 60 seconds. Reset by turning main power supply off/on.
- Overload (locked rotor) – pump shuts off. Free up rotor (or impeller) and reset by turning main power off/on.
- Motor Overheat – pump runs at reduced power until motor cools off.
- VFD Failure – pump shuts off. Attempt reset by turning main power off/on. If unable to reset replace pump (power head at least).
- Motor/Stator Failure – pump shuts off. Attempt reset by turning main power off/on. If unable to reset replace pump (powerhead at least).
Sizing and “dialing in” to match the required H/Q.
Simply stated, a line between H max at maximum RPM and head at zero flow should come close to intersecting the desired operating point.
We are replacing 3 HP basemount B&G pumps with Viridian V25s. We will connect as follows: (1) a 3″ butterfly valve will neck down to 2.5″ then connect to the suction side of the pump. (2) pump will hang (north to south) (3) Discharge will be connected to a 90 deg elbow (4) 2 1/2 inch flowcheck will be horizontal to ground (5) 2 1/2 to 3″ transition (6) 90 deg elbow up to flex connector (7) flex connector to 3′ butterfly. Is this OK? Anything we should know?
The Viridian is installed with the same considerations as any other pump – however the motor shaft needs to be horizontal and it has to be installed in a pressurized system (typical of any closed loop HVAC system). We recommend at least 3 pipe diameters of straight pipe on the inlet side of any pump install – or at the very least do not bolt a y strainer, globe valve or 90 degree elbow directly on the inlet of the pump – all pumps are happier pumping laminar (non-turbulent) fluid. The check on the discharge is OK (although as you know swing check valves can not be installed in a vertical pipe).
What are the factory defaults on a Viridian (head setting and proportional) and what do they do?
Head max is set to 23′ and proportional is 50%. This means the differential head is set to 23′ at maximum speed and the head at zero flow (dead head) is 50% of 23′ or 11.5′. Both head maz and % proportional can be adjusted to meet specific system.
What flexible coupling should be used on my frame mounted pump when a variable speed drive is controlling the motor?
We recommend a coupling that has its flexible element either bonded to the hubs or clamped securely to the hubs. The standard engaged flexible elements do not last as long, as they need to be loaded to their rating for best service.
What is the current replacement for a CE model pump?
The current replacement would be determined by the original CE model. The GPM and head conditions are also required in order to properly select the best replacement. The new CI series will not be a drop in replacement and some piping modifications will be required.
What is the current replacement for a CM pump?
The current replacement would be determined by the original CM model. The GPM and head conditions are also required in order to properly select the best replacement. The new CI series will not be a drop in replacement and some piping modifications will be required.
What is the current replacement for an FE model pump?
The current replacement would be determined by the original FE model. The GPM and head conditions are also required in order to properly select the best replacement. The new FI series will not be a drop in replacement and some piping modifications will be required.
What is the difference between a JP and a JM frame motor?
A JP motor is a close coupled pump motor where the motor shaft is the pump shaft. It has a longer shaft so that the pump can be constructed with either a soft packed seal or a mechanical seal. A JM motor is also a close coupled pump motor, however the shaft is shorter and only allows the use of a mechanical seal in the pump assembly.
What is the minimum speed of the motor of a pump controlled by a variable speed drive?
A centrifugal pump is a variable torque device where the torque is reduced with the cube of the ratio of the reduction in speed. At a low RPM there would be virtually no load on the motor. The fan in the motor should be sufficient to cool the motor.
What is the procedure for plotting the performance curve of a pump if you have an impeller diameter that falls between 2 known diameter impeller cuts?
Follow these steps to draw in a curve between 2 published pump curves with a known diameter:
- Look at the pump curves of the pump in question.
- Note the diameter of each curve on each side of the diameter curve to be plotted; i.e., FI1511 needs a curve for 10.85\\” and we need to know the head that diameter will generate at 104 GPM. 11.25\\” & 10.50\\”
- Subtract the difference between the diameters. 11.25\\” – 10.50\\” = .750\\”
- Subtract the smaller diameter from the to be drawn dia.
- Impeller 10.85\\” – 10.50\\” = .350\\”
- With a scale of 50 graduations/inch, measure the distance between the known curves. You will need to do this in equal increments along the curve to plot point to draw the curve; i.e., at 50 GPM the distance is .310\\”
- Calculate the new curve point by solving the following equation: .350\\”/.750\\” = X /.310\\”, X = .350\\”/.750\\” X .310\\”, X = .4666 X .310\\” = .145\\”
- Measure up from the lower known curve (10.50\\” dia) and plot the point. Continue with the same procedure along the curve in equal increments.
- Using a French curve, connect the plotted points to generate a smooth curve.
What size flange does the Viridian pump use?
The Viridian uses standard ANSI flanges: VR15 = 1.5 inch, VR20 = 2 inch, VR25 = 2.5 inch and VR30 = 3 inch.
What type of motor should be used with a variable speed drive?
Some manufacturers have an invert duty motor; others have made their premium efficient motor to be used with variable speed drives. These motors are called Inverter Ready.
What type of seal is the CI series pump equipped with?
Taco CI, and FI series pumps are equipped with a John Crane Type 21 mechanical seal as a standard. The stationary seat is ceramic and the rotating element mating ring is carbon. Optional seal configurations are available, including sealide C, Ni-Resist and Tungsten carbide.
Why does the seal leak when the pump runs, and stop leaking when the pump stops?
Here are some possibilities:
- Something is restricting the free movement of the seal. The product is viscous and some products become more viscous with agitation (e.g., cream becomes butter with agitation). These products are called dilatants.
- A recirculation line from the discharge of the pump is aimed at the seal and interfering with its movement.
- A foreign object is in the stuffing box. A protruding gasket is touching the movable part of the seal. The shaft is being displaced, causing the seal to hit something as it rotates, or causing the rotating face to run off the stationary face.
- The pump is operating off of its best efficiency point (B.E.P.), causing the shaft to bend. The rotating assembly is out of dynamic balance. The shaft is bent. There is misalignment between the motor and the pump. Pipe Strain is twisting the pump stuffing box. Heat causes expansion, leading to the possibility for rubbing or wear. Cavitation, slip stick, harmonic vibration, bad bearings or some other form of vibration is causing excessive movement of the shaft.
- The shaft sleeve is not concentric with the shaft, causing it to run “off center.” The pump designed with sleeve or babbitted bearings and shaft movement is excessive. The seal face is being distorted by either temperature or pressure. The product is vaporizing between the seal faces, causing the faces to blow apart. If boiler feed water vaporizes, it leaves behind all of the chemicals that were added to the water to prevent hardness, adjust PH, soften boiler scale, etc.
- In cryogenic (cold) applications, the vaporizing fluid can freeze any lubricant that might have been placed on the seal faces. This frozen lubricant can damage the carbon/graphite seal face.
Do I need an Inverter Duty Motor when my pump and motor assembly are controlled by a Variable Speed Drive?
Not necessarily, both inverter duty and inverter ready motors can be used. A centrifugal pump is a variable torque device where the torque reduces with the cube of the ratio of the speed. Baldor has designed their Super E motor with special insulated wire that allows the windings to pass the Corona Inception Voltage test. These windings pass the requirements of NEMA MG 1 Part 31 for peak voltage (1600 volt peaks) when used on inverters. These motors are labeled Inverter Ready. NEMA Part 31, Definit -Purpose Inverter Motors, lists many requirements other than just peak voltage.
A true Inverter Duty Motor meets all the requirements of Part 31 and is expected to perform satisfactorily for torque, temperature, noise and vibration over the entire speed range. This applies to constant torque applications. A pump is a variable torque application and only concerns us with the 1600 volt peaks produced by the VSD. The temperature, noise and vibration reduce as the motor slows and unloads. These will not be factors for pump applications.